Note that the number of total possible outcomes is equal to the sample space of the first die 6 multiplied by the sample space of the second die 6 which is 36.
Roll a die 36 times compute the probability of obtaining exactly 6 sixes.
Also there are 6 choose 2 15 different ways to arrange the rolls.
P 3 1 6 ⁿ 1 2 ⁿ.
You need to roll exactly 2 sixes and 4 other numbers.
So to get a 6 when rolling a six sided die probability 1 6 0 167 or 16 7 percent chance.
The roll has 6 sides the probability of rolling a six when the die is rolled once is 1 6 when rolled 4 times each time has a probability of 1 6.
So the probability is.
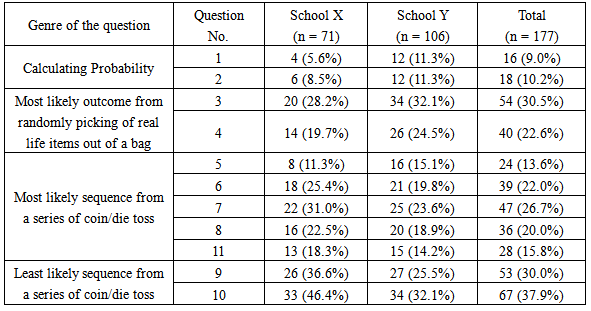
Probability table of rolling two dice.
Independent probabilities are calculated using.
15 1 6 2 5 6 4 0 20094.
Then the probability is.
The probability of rolling exactly x same values equal to y out of the set imagine you have a set of seven 12 sided dice and you want to know the chance of.
Probability of both probability of outcome one probability of outcome two so to get two 6s when rolling two dice probability 1 6 1 6 1 36 1 36 0 0278 or 2 78 percent.
The probability that we roll exactly one six is 3 the number of ways to choose which one will be a six the number of one set regions in the diagram times the probability that that roll will be a six 1 6 times the probability that the other two rolls will not be six 5 6 5 6.
The probability of rolling a six on one roll is 1 6.
The possible outcomes of rolling two dice are represented in the table below.